PROJECT OVERVIEW
The current time-entry process is manual and error-prone, making it difficult for legal professionals to track time across multiple projects accurately.
As a result, they often miss billable hours or make mistakes — which leads to delayed payments, lost revenue, and added stress.
Time pressure only makes it worse, with users often forgetting or misclassifying tasks, which damages their productivity and professional integrity. Without automation to help them organize and prioritize tasks, the system increases mental load and operational inefficiency.
This project will reduce registration errors, save users significant hours, and ensure training can be completed reliably across nearly 300 programs.
How can we simplify the time-entry process so professionals can focus on their work, not logging it?
Where does the current system fall short in capturing fragmented tasks or work tracked in 6 or 10-minute increments?
How could reducing these gaps improve both user confidence and billing accuracy?
I addressed these challenges through research, resulting in 3 strategic aims:
🎯 Redesign Time-Entry for Efficiency
Streamline time-entry by exploring passive tracking methods that reduce user effort and improve logging accuracy
🎯 Validate Interactive Solutions with Real Users
Test wireframes to ensure they address user needs and pain points, especially around automation.
🎯 Identify Unmet User Needs in Time-Entry
Uncover user pain points to improve task tracking and reduce cognitive load.

Budget
$150,000

Team
Lead UX Researcher, 2 UX Designers
Innovation Team

Timeline
8 weeks
Research Goals & Approach
We used a phased research approach that combined discovery and evaluative methods to uncover unmet user needs and validate assistive time-entry concepts. Our goal was to ensure the proposed solutions reduce user burden and improve billing accuracy.
RG1: Identify unmet user needs and pain points across the time-entry journey, including fragmented tasks and micro-increment tracking.
RG2: Evaluate time-entry interactions to determine if they reduce cognitive effort and improve task classification accuracy.
RG3: Validate assistive time-entry solutions for simplifying workflows and reducing manual user burden.
RG4: Evaluate wireframes for key billing behaviors, including retroactive logging, batch entry, and 6–10 minute task tracking.
Stakeholder Interviews
Requirements Gathering
Strategic Goal Alignment
Assumption Mapping Workshop
Collaborative Journey Visualization
Prioritization Workshop
13 1:1 User Interviews
13 Wireframe Usability Tests (in-session)
Surveys
Thematic Analysis
Roadmap Prioritization Workshops
Design Proposal Development
Internal & External Stakeholder Presentations
⚙️Process | 📦 Artifacts ▸
Intent
Align stakeholders and define targeted research to uncover user workflow inefficiencies.
Establish a rigorous, user-focused discovery framework to guide design strategy.
⚙️ Defined targeted research goals on task fragmentation, cognitive load, and billing behaviors to uncover user workflow inefficiencies.
⚙️ Synthesized early insights into testable hypotheses to inform and accelerate design phase decisions.
⚙️ Clarified research scope and priorities to focus efforts on critical user inefficiencies.
📦 Current-State Workflows, Problem & Opportunity Statements
⚙️Process | 📦 Artifacts ▸
Intent
Challenge assumptions and map workflows to identify high-impact opportunities that inform design direction.
⚙️ Facilitated assumption mapping workshops using “How Might We” frameworks to expose team biases and align on problem framing.
⚙️ Created journey visualizations with cross-functional teams to clarify user workflows and expose friction points.
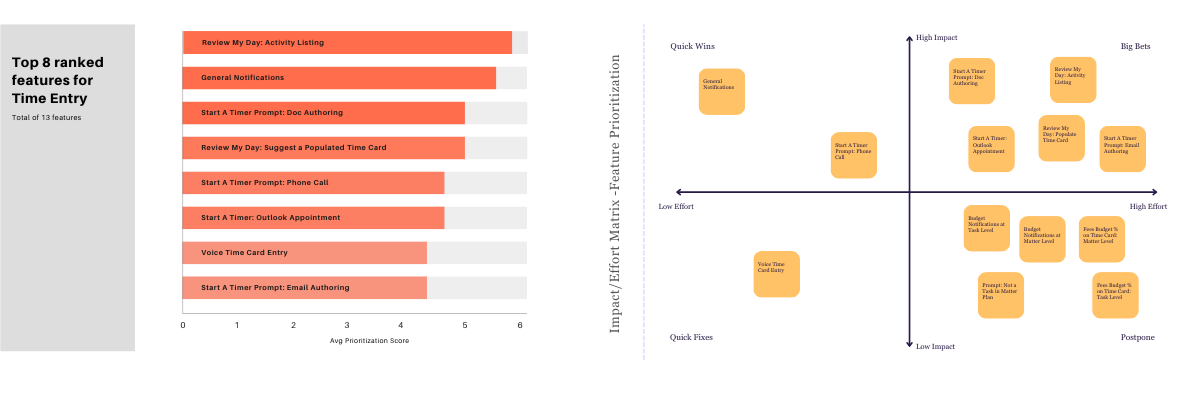
⚙️ Prioritized opportunity areas using impact-effort matrices to balance user value and feasibility, and business goals.
⚙️ Aligned stakeholders around key problems to support design ideation and team commitment.
📦 Assumption Maps, Prioritization Matrices
⚙️Process | 📦 Artifacts ▸
Intent
Apply a mixed-methods approach to uncover user needs, validate wireframes, and align solutions with real workflows.
⚙️ Conducted 13 1:1 interviews and in-session wireframe usability tests, with platform users, to uncover pain points and validate solutions.
⚙️ Deployed surveys to quantify unmet needs and validate qualitative insights for data-driven decisions.
⚙️ Analyzed themes to reveal recurring user pain points and behaviors, guiding design prioritization.
⚙️ Facilitated a prioritization workshop to translate insights into actionable opportunities ranked by user impact and feasibility.
📦 Interview Guide, Wireframes, Survey Results, Thematic Analysis, Prioritization Matrix
⚙️Process | 📦 Artifacts ▸
Intent
Translate research insights into strategic design proposals aligned with user needs and business goals.
⚙️ Led roadmap workshops with stakeholders to prioritize features based on identified user needs and business value.
⚙️ Developed design proposals addressing validated pain points and aligning cross-functional teams around implementation.
⚙️ Presented solutions to internal and external stakeholders to build buy-in and ensure shared understanding.
📦 Roadmap Prioritization Document, Design Proposal, Presentations
Challenges
Repositioned research as a driver of discovery and early design iteration.
Framed insights as opportunity space, enabling broader concept development.
Connected discoveries to workflow needs to guide design direction.
I juggle dozens of tasks every hour - it’s overwhelming to keep track.
Missing a few means lost hours, billing errors, and stress trying to fix it.
– Candidate 9
Key Discoveries
Recovering lost time
Insight 1: Users lose work hours when they forget to log work, creating frustration. This leads to errors in task records. ▸
- Retroactive entry solves lost time problem.
- Users can accurately fill missed details without friction.
Solution 1: Make retroactive time-entry quick and easy to use. ▸
- Recover lost work hours quickly and effortlessly.
- Prevent errors and billing mistakes, restoring user confidence.
- Reduce frustration from missed or incorrect entries.
Lack of relevant guidance
Insight 2: Users struggle to manage tasks without guidance. This causes frustration and missed time entries. ▸
- Notifications for user actions were missing.
- Existing solution didn’t support starting, stopping, or switching tasks.
Solution 2: Provide contextual prompts that guide task management. ▸
- Increase task accuracy when users need to start, stop, or switch tasks.
- Reduce errors & cognitive load with clear, actionable guidance.
- Give users control over task flow and adjustments.
Manual control preference
Insight 3: Automated time suggestions are error-prone, causing frustration. Users want more control to prevent errors. ▸
- Automated entries based on calendar events were unreliable.
- Users need manual adjustment to prevent mistakes.
Solution 3: Enable manual prompts with optional low-risk automation. ▸
- Give users control over adjusting and extending time entries.
- Enable users to correct automated entries, reducing mistakes and errors.
- Improve task logging accuracy.
Accessibility through voice commands
Insight 4: Mandatory voice input risks privacy. Users want optional voice commands to complete tasks safely. ▸
They scan for:
- Users want control over when to use voice input to protect privacy.
- Mandatory voice input causes unease and hesitancy, limiting adoption.
Solution 4: Offer optional voice input alongside manual entry.This gives users control over privacy and task flow. ▸
- Let users choose manual or voice input per preference.
- Maintain privacy protection while enabling voice commands.
- Allow fast task initiation with voice input.
- Provide alternatives to voice-only input for flexibility.